Library Creations and structure:
- Create Libraries based on business functions. E.g. HR, Marketing, Finance, Management etc. if required libraries on the individual sites can also be created based on document categories e.g. contracts, accounts payable/receivable etc.
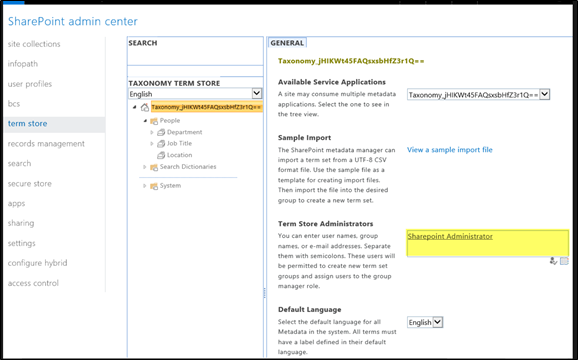
- Create and implement organizational meta data strategy and structure through Term Store feature in SharePoint. This allows for standard across the organization in the usage of meta data terms.
Example of Organizational Term Store
- Use Meta Data columns, instead of folders. Use of meta data helps in the following:
- Search (it makes it easier for SharePoint search to index items with meta data rather than folders)
- Sorting items (ascending or descending)
- Grouping items by category
- Creating views for document libraries
Example of SharePoint Library with Folder Structure

Example of SharePoint Library with Meta Data Column Structure (Country, State, City)
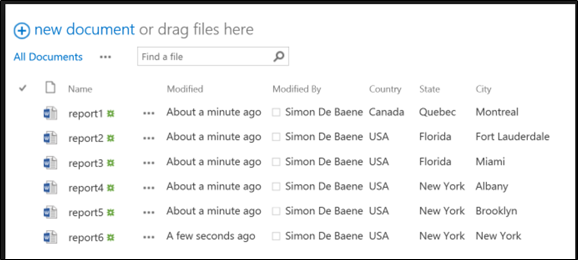
- Do not use more than 12 meta data columns in a document library. This includes people, lookup and managed meta data column.
- Create organization wide document naming convention and train users in its usage and implementation.
- Versioning of document should be enabled on a need basis. The number of major and minor version should be determined for each library/document category and implemented accordingly. Blanket versioning leads to too many versions of the same documents, thereby causing greater storage needs, cost and causes sync issues.
- Library sync to user’s local computer should be implemented on need basis. This prevents proliferation of information and allows for greater security around organizational data.
- By default, the document library list view threshold is 5000 documents, although a document library can hold up to 30,000,000 documents. Libraries that have documents above 5000, start having performance issues in terms of loading, sorting etc. It is recommended to create groups or views for such libraries.
- Documents that are old and is not required by users should be archived. An archival policy should be created based on the document type and documents should be archived based on the policy. A record center solution within SharePoint can be used for archival purposes. This will help in keeping the library clean and enhancing the performance.
- A view is a custom representation of how the items in a document library is displayed when a user navigates to a library. An example of a view is display of only those documents that a user has created.
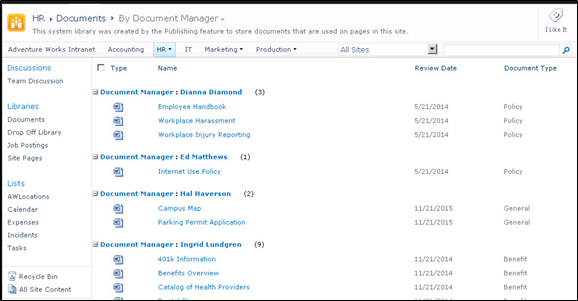
- For ease of search and sorting it is recommended to group documents. This allows for similar types of documents to be displayed together as a group. An example is group by document types, invoices, contracts etc.
Example of documents have been grouped by Document Manager (Owners)
- The maximum size of a document that can be uploaded to a SharePoint document library is 100GB for SharePoint 2016 and 2 GB for SharePoint 2013 version.
- A maximum of 100 documents can be uploaded to a SharePoint document library via drag and drop method.
Document library security considerations:
- Create organizational information access and usage documentation. This document should detail users access rights to various information on the SharePoint and the libraries within the application. These rights can be read, contribute, edit, design and full. This document should be updated as needed.
- Ensure users have access to information based on their role within the organization. If a user should not be deleting a document within a library, he/she should not have delete rights to that document library.
- Implement user access and role at the library level. Until and unless absolutely required do not create unique user access rights at the folder or document level.
- If access to certain category of document require unique permission or access to such documents needs to be locked down, in that case the user should create a new document library for such categories of documents.
- If documents are to be shared with users outside the organization, a copy of these documents should be saved in a separate document library and shared, instead of randomly sharing or sending links from the existing libraries.
- All document shared should have an expiry period. Documents should not be shared for long durations with users outside the organization.
- User access to libraries should be periodically audited and updated as needed.
User Permissions in SharePoint:
These are the out of box permission types in SharePoint. Besides these SharePoint also allows creation of groups with custom permissions. Of all the permission listed below the most commonly used are, Full Control, Design, Edit, Contribute, Read and View only rights.
| Permission Type | Allowed Actions |
| Full Control | Gives user full control over the site/library/list |
| Design | A user can view, add, update, delete, approve, and customize. |
| Edit | A user can add, edit and delete lists; can view, add, update and delete list items and documents. |
| Contribute | A user can view, add, update, and delete list items and documents. |
| Read | A user can view pages and list items and download documents. |
| Create new subsites | A user can create new subsites |
| View Only | A user can view pages, list items, and documents. Document types with server-side file handlers can be viewed in the browser but not downloaded. |
| Approve | A user can edit and approve pages, list items, and documents. |
| Manage Hierarchy | A user can create sites and edit pages, list items, and documents. |
| Restricted Read | A user can view pages and documents but cannot view historical versions or user permissions. |
| Restricted Interfaces for Translation | A user can open lists and folders, and use remote interfaces. |
Document level considerations:
- SharePoint online allows file upload of all types and formats. The following code extension files, however requires custom script settings to be enabled.
| File extension | File type |
| .aspx | ASP.NET Active server page |
| .asmx | ASP.NET web services source file |
| .ascx | ASP.NET wep user control file |
| .master | ASP.NET master web page |
| .xap | Windows phone installation |
| .swf | ShockWave Flash |
| .jar | Java archive |
| .xsf | Office InfoPath form definition file |
| .htc | HTML Component file |
- The following characters types are not allowed in OneDrive or SharePoint online. These characters will create issues with file upload and sync features. ” * : < > ? / \ |
- Following file and folder names are not supported in OneDrive or SharePoint: .lock, CON, PRN, AUX, NUL, COM1 – COM9, LPT1 – LPT9, _vti_, desktop.ini
- Any file name starting with ~$ is also not supported.
- Other consideration:
- “_vti_” cannot appear anywhere in a file name
- “forms” isn’t supported when the folder is at the root level for a library.
- You can’t create a folder name in SharePoint Online that begins with a tilde (~).
- File Name and Path Limitations: Any document name or the file path length (URL) should not exceed 400 characters.
References:
- Microsoft



